Surety Bond
A contract whereby a party called SURETY, guarantees, for a consideration, the performance by another party called the PRINCIPAL of an obligation or undertaking in favor of a THIRD PARTY called OBLIGEE.
Surety bond or guaranty involves a promise by one party to assume responsibility for the debt obligation of a borrower if that borrower defaults
Surety underwriters collect specific financial, legal and other pertinent information about customers applying for insurance. They evaluate this information and calculate risk based on established criteria. The ability of the applicant to perform his obligation is one criterion.
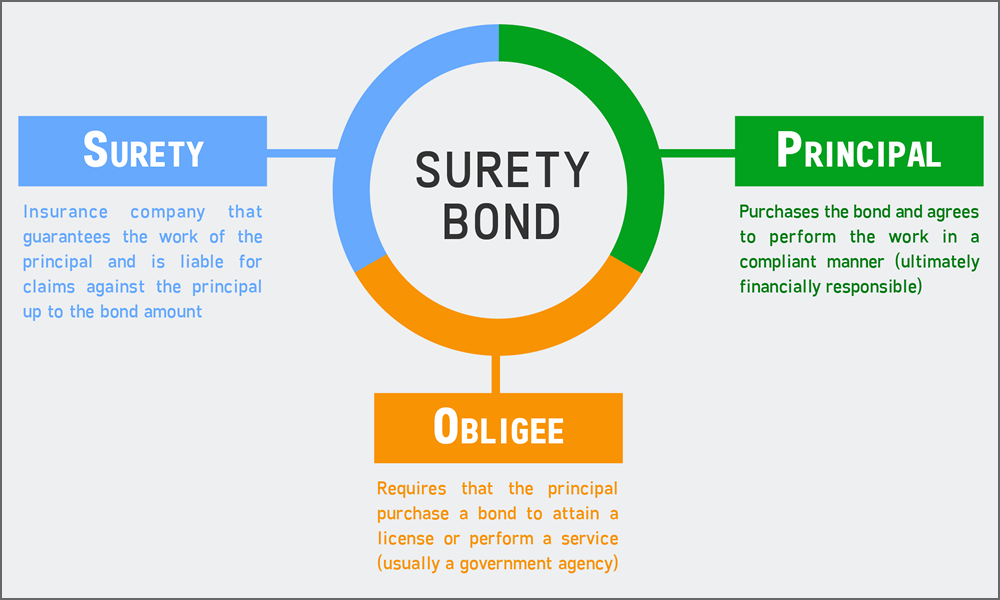
A surety bond can be defined in its simplest form as a written agreement to guarantee compliance, payment, or performance of an act. Surety is a unique type of insurance because it involves a three-party agreement. The three parties in a surety agreement are:
- Principal – the party that purchases the bond and undertakes an obligation to perform an act as promised.
- Surety – the insurance company or surety company that guarantees the obligation will be performed. If the principal fails to perform the act as promised, the surety is contractually liable for losses sustained.
- Obligee – the party who requires, and often receives the benefit of— the surety bond. For most surety bonds, the obligee is a local, state or federal government organization.